Malware and ransomware
Block email attacks that deliver or link to files that execute malicious code.
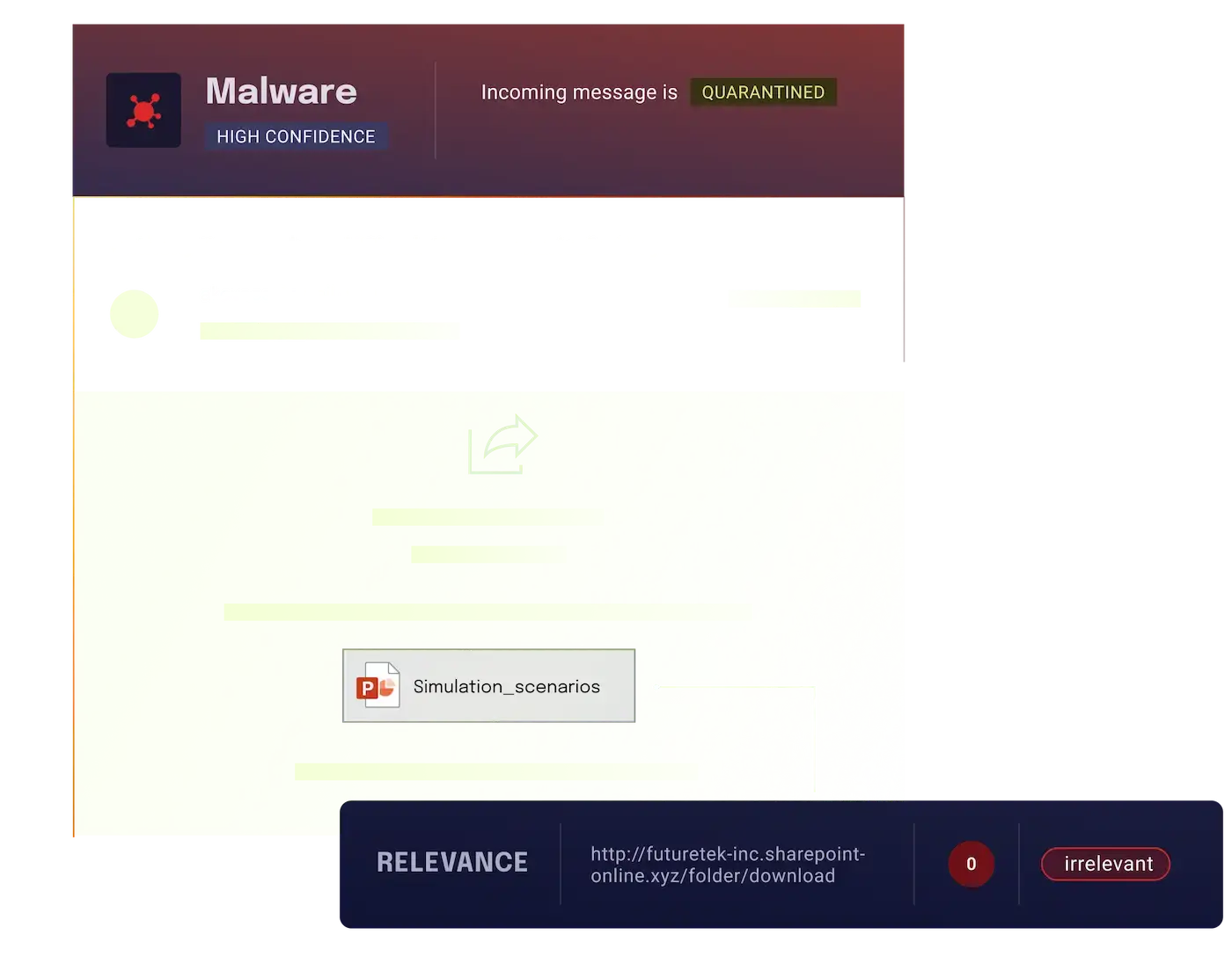
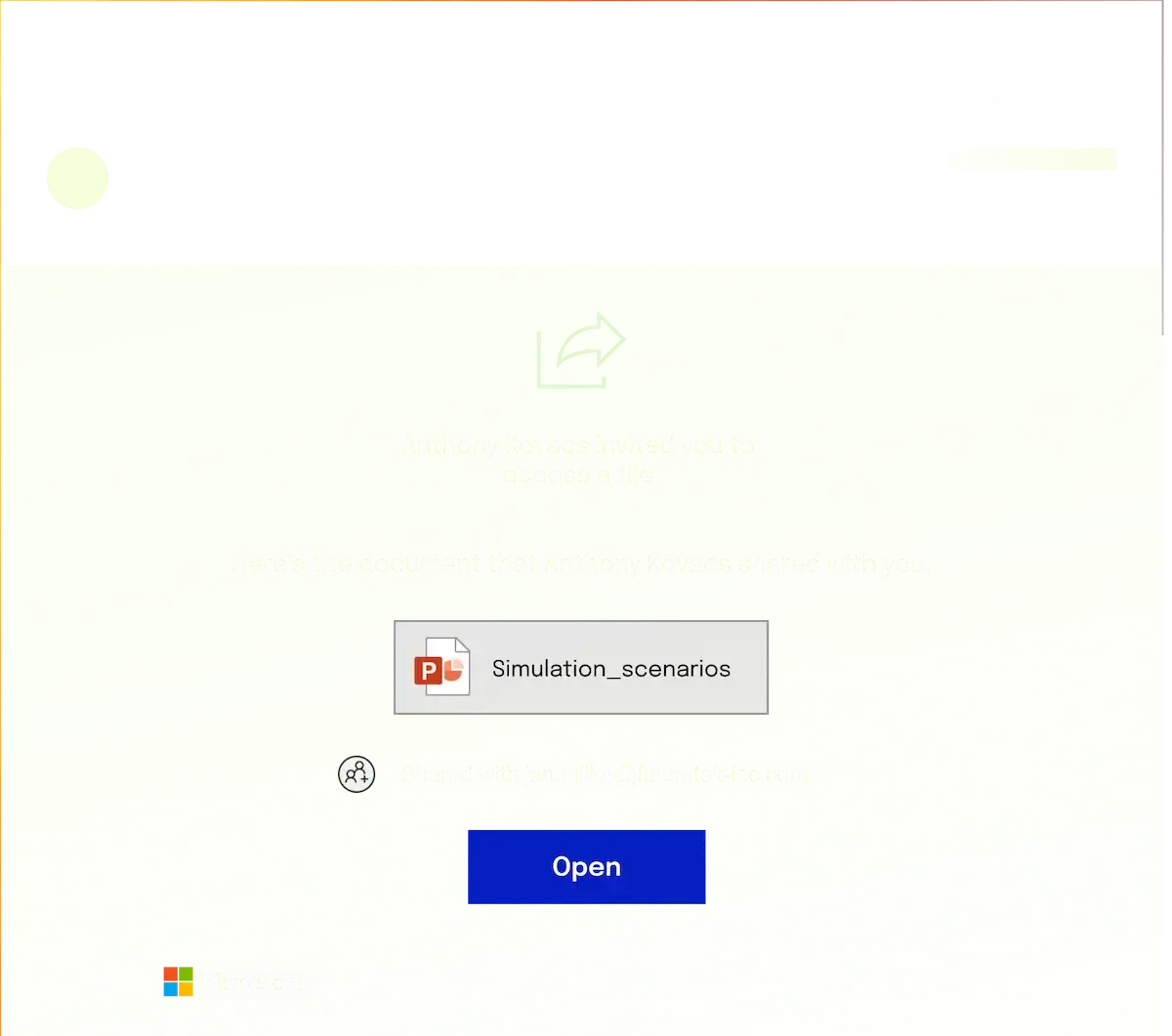
Legitimate links to malicious files and encrypted file formats evade detection
Malware and ransomware attacks are increasingly bypassing traditional defenses by linking to malicious files hosted on legitimate platforms or sending encrypted formats.
Instead of attaching harmful files directly, attackers use trusted platforms such as SharePoint, Google Drive, or Dropbox to host malicious content and trick users into downloading infected files. Encrypted file formats further hide these threats, making them more difficult to detect.
Once accessed, these files exploit system vulnerabilities, either immediately compromising systems or lying dormant. Ransomware often follows, encrypting files and demanding payment.
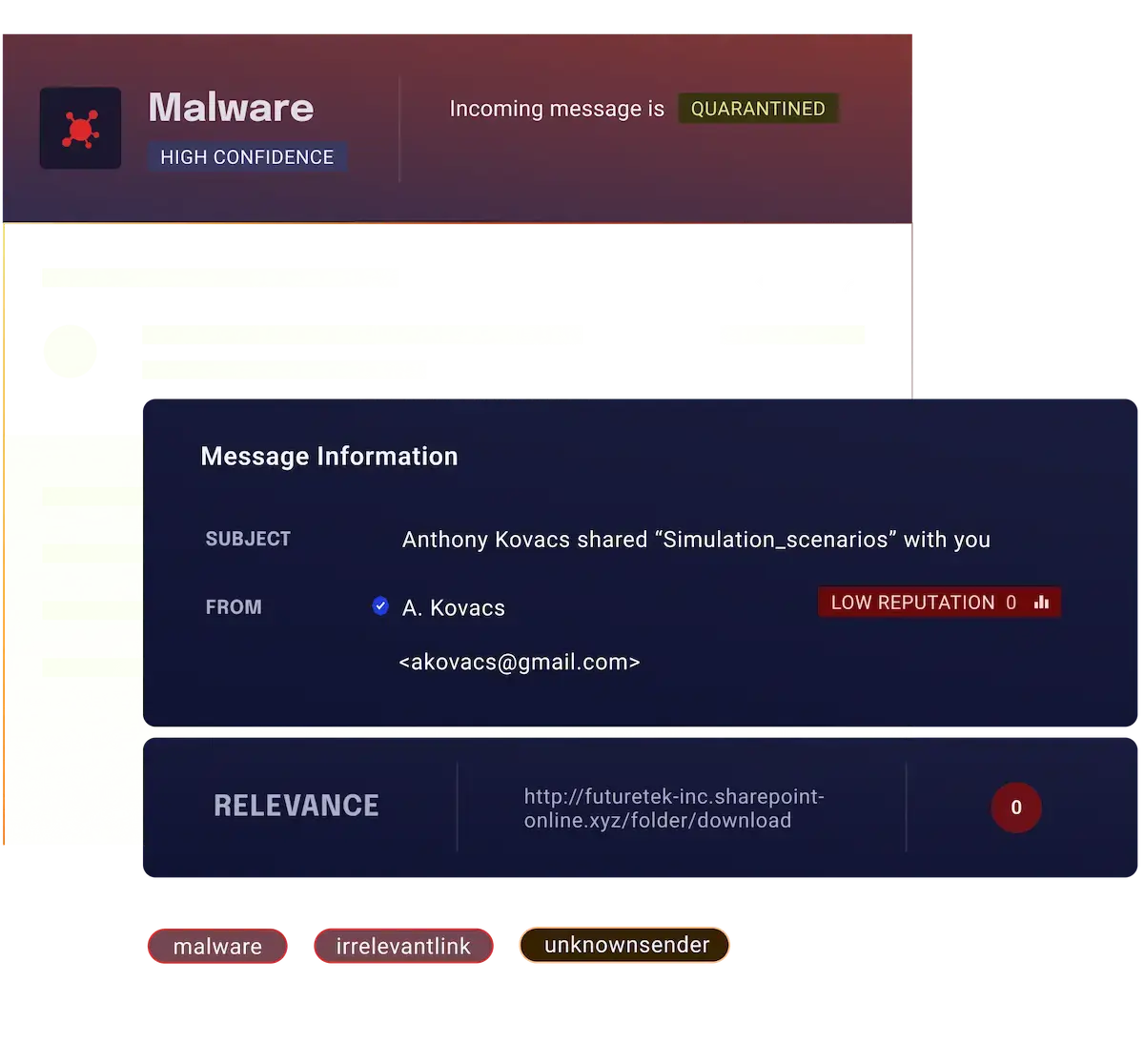
How xorlab detects and blocks malware and ransomware
xorlab detects and blocks malware and ransomware emails without relying on known malicious file signatures or traditional security indicators.
The xorlab Security Platform:
-
Learns communication patterns between senders and recipients, considering file formats, extensions, and content to identify unusual activity.
-
Analyzes document files in a dynamic sandbox, catching malware that bypasses standard static filters.
-
Prompts users for passwords to encrypted files, enabling thorough analysis for potential threats.
Malware and ransomware techniques and characteristics
Document-based malware
Attackers embed VBA scripts or macros in documents to execute malicious code when opened.
File-based exploits
Emails link to files designed to exploit software vulnerabilities in the victim’s system.
File-droppers
A downloaded benign file will download and execute additional malicious code.
Encryption and obfuscation
Files are encrypted or disguised in archives to make them harder to detect.
External file links
Linked files are hosted on cloud services or compromised sites to appear legitimate.
Within the MITRE ATT&CK® Matrix, malware and ransomware maps to multiple techniques (Phishing (sub-technique: Spearphishing Attachment, Link, via Service), User Execution (sub-technique: Malicious File), Command and Scripting Interpreter, etc.) and tactical objectives (Initial Access, Execution, Lateral Movement, Collection, Command and Control, Exfiltration and Impact).
Resource center
Ciso Guide
Explore our ebook about smarter email security – an attacker-centric, proactive approach.
News
How attackers leverage the trust of GitHub to launch targeted phishing attacks.
Attack simulation
Stress test your email security with our realistic email attack simulation.
Pen-test your email security
False negatives causing extra work? Unsure of your protection against malware and ransomware? Identify gaps with xorlab's Email Attack Simulation.
Trusted by leading organizations — from 500 to 37,000 employees

















